As a Canadian medical physician, financial planning is essential to ensure long-term security and stability. One of the most important decisions you will face is how to save for retirement effectively. Two popular options are the Individual Pension Plan (IPP) and the Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP). Each has its advantages and drawbacks, and understanding the nuances can help you make an informed decision.
Understanding the RRSP
What is an RRSP?
The RRSP is a tax-advantaged savings vehicle available to all Canadian taxpayers. Contributions to an RRSP are tax-deductible, and the funds grow tax-deferred until withdrawal. Physicians, like other high-income professionals, often use RRSPs to lower their taxable income while saving for retirement.
Key Benefits of an RRSP
- Tax Deferral: Contributions reduce taxable income, deferring tax until withdrawal.
- Flexibility: You can invest in a variety of asset classes.
- Spousal Contributions: Allows income splitting through spousal RRSPs.
- No Employer Obligation: You have complete control over contributions.
- Withdrawals: Funds can be accessed at any time, though subject to tax.
Limitations of an RRSP
- Contribution Limits: Maximum annual contribution is 18% of earned income, up to a specified limit ($31,560 for 2024).
- Forced Withdrawals: At age 71, the RRSP must be converted to a Registered Retirement Income Fund (RRIF), with mandatory withdrawals.
- Market Risk: Investments are subject to market fluctuations.
Understanding the IPP
What is an IPP?
An IPP is a defined benefit pension plan designed for incorporated professionals, such as physicians, who own their medical professional corporations (MPCs). It is an employer-sponsored plan that allows for higher tax-advantaged retirement savings than an RRSP.
Key Benefits of an IPP
- Higher Contribution Limits: Allows for greater tax-deferral compared to an RRSP, especially for physicians over 40.
- Defined Benefits: Provides predictable retirement income based on years of service and earnings.
- Additional Tax Deductions: Contributions are tax-deductible for the corporation.
- Creditor Protection: Assets in an IPP are generally more protected from creditors than RRSPs.
- Post-Retirement Contributions: Potential for additional funding through past service contributions and terminal funding.
Limitations of an IPP
- Complex Setup: Requires actuarial involvement and annual compliance costs.
- Less Flexibility: Locked-in structure limits access to funds before retirement.
- Corporation Required: Only available to incorporated physicians.
- Investment Restrictions: Subject to government regulations on pension fund management.
Comparing IPP and RRSP for Physicians
Contribution Limits Comparison
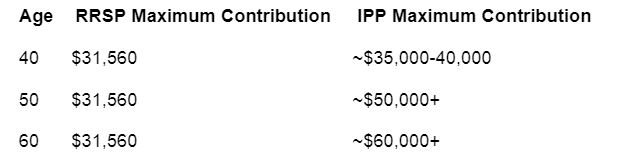
As seen above, IPPs allow significantly higher contributions as physicians age, making them advantageous for those in their late 40s and beyond.
Tax Considerations
- RRSPs: Contributions reduce personal taxable income, with withdrawals taxed at marginal rates.
- IPPs: Contributions are made by the corporation, reducing corporate tax liability, and withdrawals are taxed as personal income in retirement.
Administration & Costs
- RRSPs: Low-cost and easy to manage.
- IPPs: Require setup fees ($5,000-$7,000) and annual actuarial filings (~$1,500+ per year).
Flexibility
- RRSPs: Allow easier access to funds, making them ideal for short-term liquidity needs.
- IPPs: Designed for long-term retirement income security but lack flexibility in early withdrawals.
When Should a Physician Choose an IPP Over an RRSP?
- Age 40+: Physicians in their 40s and older benefit from higher contribution limits.
- Stable and High Income: An IPP is more beneficial for those with consistent income and corporate surplus.
- Long-Term Planning: Ideal for physicians who intend to remain incorporated until retirement.
- Estate Planning: IPPs allow assets to be transferred to a spouse tax-efficiently upon death.
Final Thoughts
For younger physicians or those who prioritize flexibility, an RRSP may be the best option. However, for incorporated physicians over 40 with stable income and long-term retirement goals, an IPP offers superior tax efficiency and retirement savings potential. Please speak with your Heritage MD advisor when evaluating your personal financial circumstances, tax strategies, and retirement objectives as this will help determine the best choice.

